Week By Pregnancy: From Conception to Birth
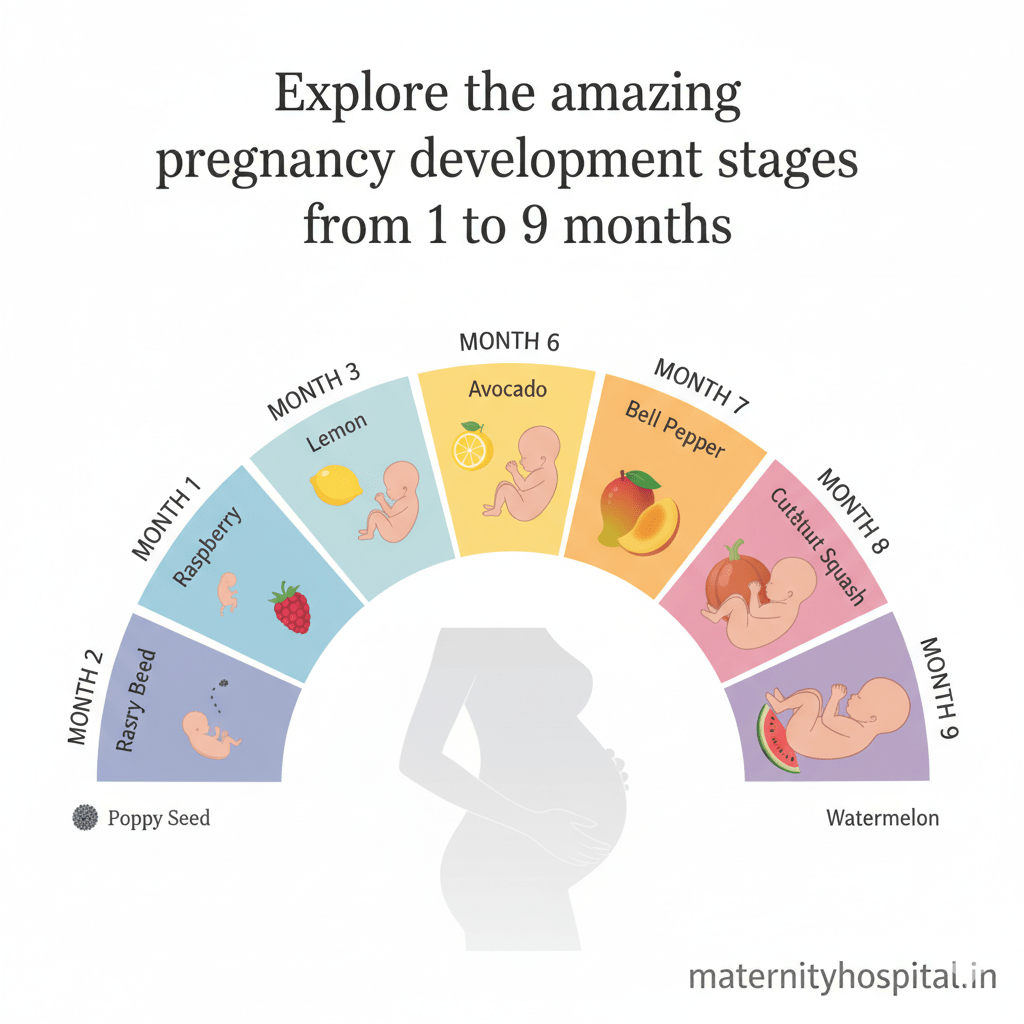
Week by Pregnancy Fetal development is an incredible journey that begins with conception and continues until birth. Throughout the 40 weeks of pregnancy, the baby undergoes significant transformations. This guide provides a week-by-week breakdown of fetal growth, ensuring expecting parents are informed at every stage.
First Trimester (Week 1-12)
1-2: Conception and Implantation
- Pregnancy begins when the sperm fertilizes the egg in the fallopian tube.
- The fertilized egg (zygote) divides rapidly and travels to the uterus.
- By the end of week 2, implantation occurs, and the placenta starts forming.
3-4 : Embryo Formation Begins
- The fertilized egg embeds in the uterine lining.
- The amniotic sac and placenta begin forming to support the baby’s growth.
- Basic structures like the neural tube (which forms the brain and spinal cord) start developing.
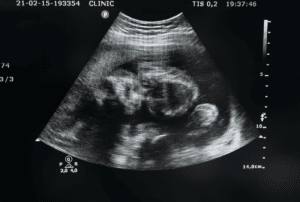
5 and 6: Heartbeat and Organ Development
- The heart starts beating, and the circulatory system forms.
- The embryo is about the size of a sesame seed.
- Limb buds appear, and facial features start forming.
7 and 8: Rapid Brain Development
- The brain and nervous system develop rapidly.
- Fingers and toes start forming but remain slightly webbed.
- Eyelids and ears become more defined.
9-12 : Fully Formed Fetus
- Bones begin to harden, and muscles start functioning.
- At this stage, the baby starts making small movements, and while these may not yet be felt by the mother, they indicate growing muscle strength. Additionally, the genitalia begin developing, although they might not be distinguishable during an ultrasound just yet.
Second Trimester (Week 13-26)
13-16: Growth and Strength
- The baby grows rapidly, reaching about 4 inches in length.
- Fingerprints develop, and the baby begins practicing swallowing.
- Lanugo (fine hair) starts covering the body.
17-20: Movements Become Noticeable
- The mother may start feeling fetal movements, called “quickening.”
- The baby starts producing meconium (first stool).
- A protective layer called vernix caseosa forms over the skin.
21-24: Sensory Development
- The baby’s taste buds develop, and they can hear external sounds.
- Eyelids start opening, and rapid eye movement (REM) begins.
- Lungs start producing surfactant, crucial for breathing after birth.
25-26: Increased Survival Rate
- The baby responds to light and sound.
- The lungs and other vital organs continue maturing.
- The baby is about 13-14 inches long and weighs around 2 pounds.
27-30: Stronger Kicks and Brain Development
- The baby’s kicks and movements become more noticeable.
- The brain continues rapid development, forming neural connections.
- The baby starts storing fat under the skin.
31-34: Gaining Weight
- The baby’s bones are fully developed but still soft.
- The immune system strengthens, and the baby gains weight rapidly.
- The baby starts practicing breathing movements.
35-37: Preparing for Birth
- The baby’s head may move into the birth position (head-down).
- The digestive system is fully developed.
- Most babies born at this stage can survive with medical assistance.
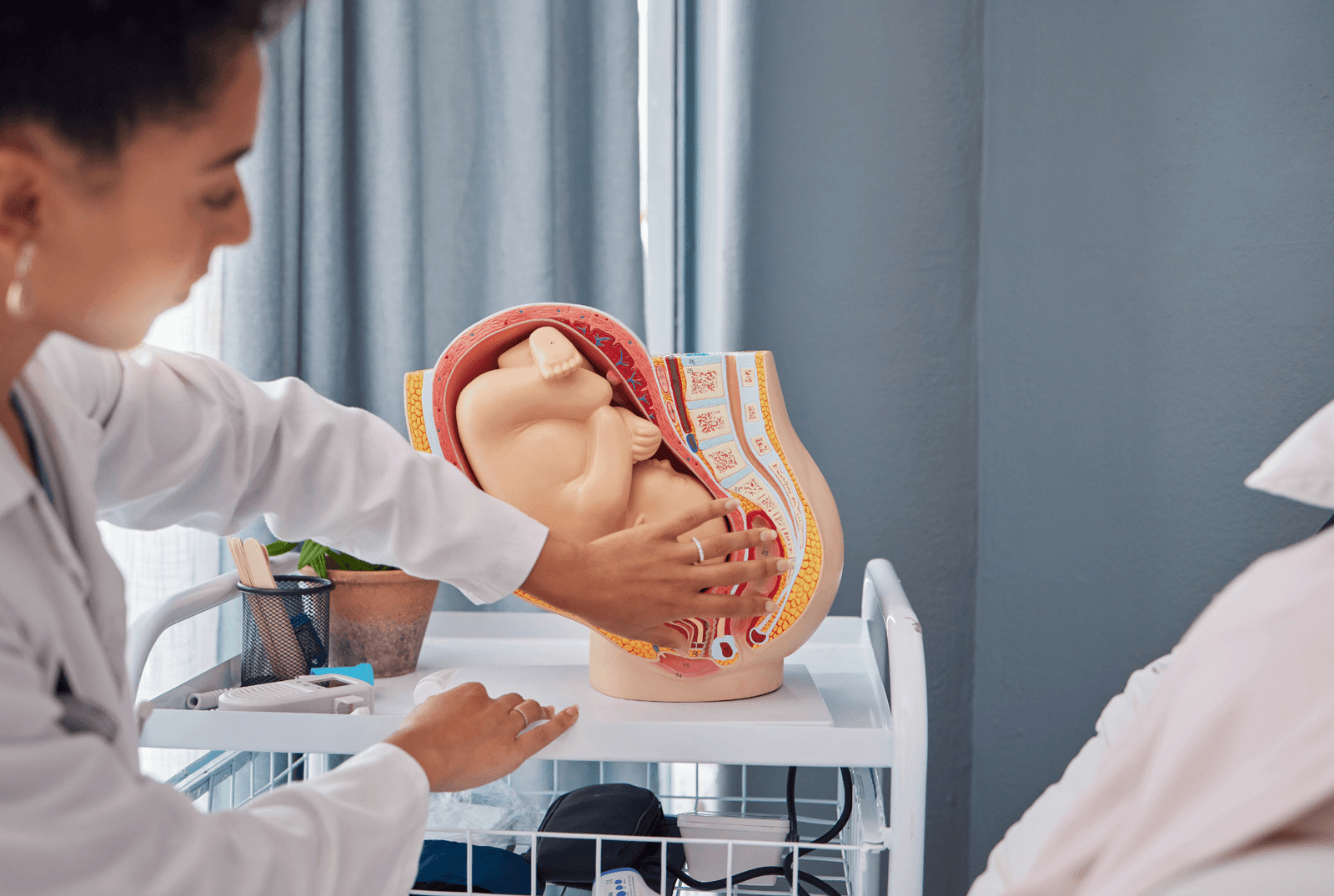
38-40: Ready for Birth
- The baby is fully developed and ready to be born.
- The lungs are mature, and the baby practices sucking and swallowing.
- At birth, the average baby weighs between 6-9 pounds and measures around 19-21 inches.
Essential Prenatal Care for Each Trimester
- First Trimester: Take prenatal vitamins, avoid harmful substances, and schedule your first ultrasound.
- Second Trimester: Monitor fetal movements, maintain a healthy diet, and start light exercises.
- Third Trimester: Attend regular check-ups, prepare for labor, and track baby’s movements.
FAQs on Fetal Development
1. When does a baby’s heart start beating?
The baby’s heart starts beating around week 5-6 and is detectable via ultrasound.
2. When can I feel my baby move?
Most mothers feel the baby move between week 16-22 (second trimester).
3. How much does the baby weigh at birth?
At birth, a full-term baby usually weighs between 6-9 pounds.
4. What foods support fetal development?
A diet rich in folic acid, calcium, iron, and protein supports healthy growth. Include leafy greens, dairy, lean meats, and nuts.
5. What should I avoid during pregnancy?
Avoid alcohol, smoking, raw seafood, unpasteurized dairy, and excessive caffeine to prevent complications.
Week By Pregnancy External Resources for Further Reading
Mayo Clinic – Fetal Development Stages
WebMD – Pregnancy Week-by-Week Guide
American Pregnancy Association – Prenatal Care
Understanding fetal development week by week helps parents feel more prepared and reassured throughout pregnancy. Regular prenatal care and healthy habits ensure a smooth journey toward welcoming a new life!