Radiological Tests During Pregnancy
Are Radiological Tests Safe During Pregnancy? A Complete Guide for Expectant Mothers
Pregnancy is a remarkable and delicate journey, and the health of both the mother and the growing baby is a top priority. One common concern among expectant mothers is “radiological tests during pregnancy?”
This question can spark anxiety for many expecting parents. Let’s break down the facts, myths, and medical insights around radiological imaging during pregnancy so you can make informed and confident decisions about your healthcare.
Why Are Radiological Tests a Concern During Pregnancy?
Radiological procedures are powerful diagnostic tools. However, many of them involve ionizing radiation (X-rays, CT scans) or strong magnetic fields (MRI). Understandably, expecting mothers worry about possible effects on the developing fetus.
Here’s why:
- Ionizing radiation can potentially alter cellular DNA at high doses.
- The risk to the fetus depends on:
✅ Type of test
✅ Radiation dose
✅ Stage of pregnancy - Modern healthcare minimizes these risks with advanced technology, shielding, and alternative imaging options.
Key Point: Most diagnostic imaging involves radiation doses far below levels associated with fetal harm.
🗓️ Pregnancy Trimester and Sensitivity to Radiation
The stage of pregnancy plays a critical role in determining fetal sensitivity to radiation:
Early Pregnancy (Weeks 1–12)
- The most vulnerable period because organs and tissues are forming (organogenesis).
- Unnecessary exposure is strongly avoided.
Mid-Pregnancy (Weeks 13–26)
- The fetus becomes less sensitive compared to the first trimester, and doctors can perform certain tests while taking appropriate precautions.
Late Pregnancy (Weeks 27–40)
- Radiation risk reduces significantly in this stage, but healthcare providers still advise caution.
📸 Common Radiological Tests and Pregnancy Safety
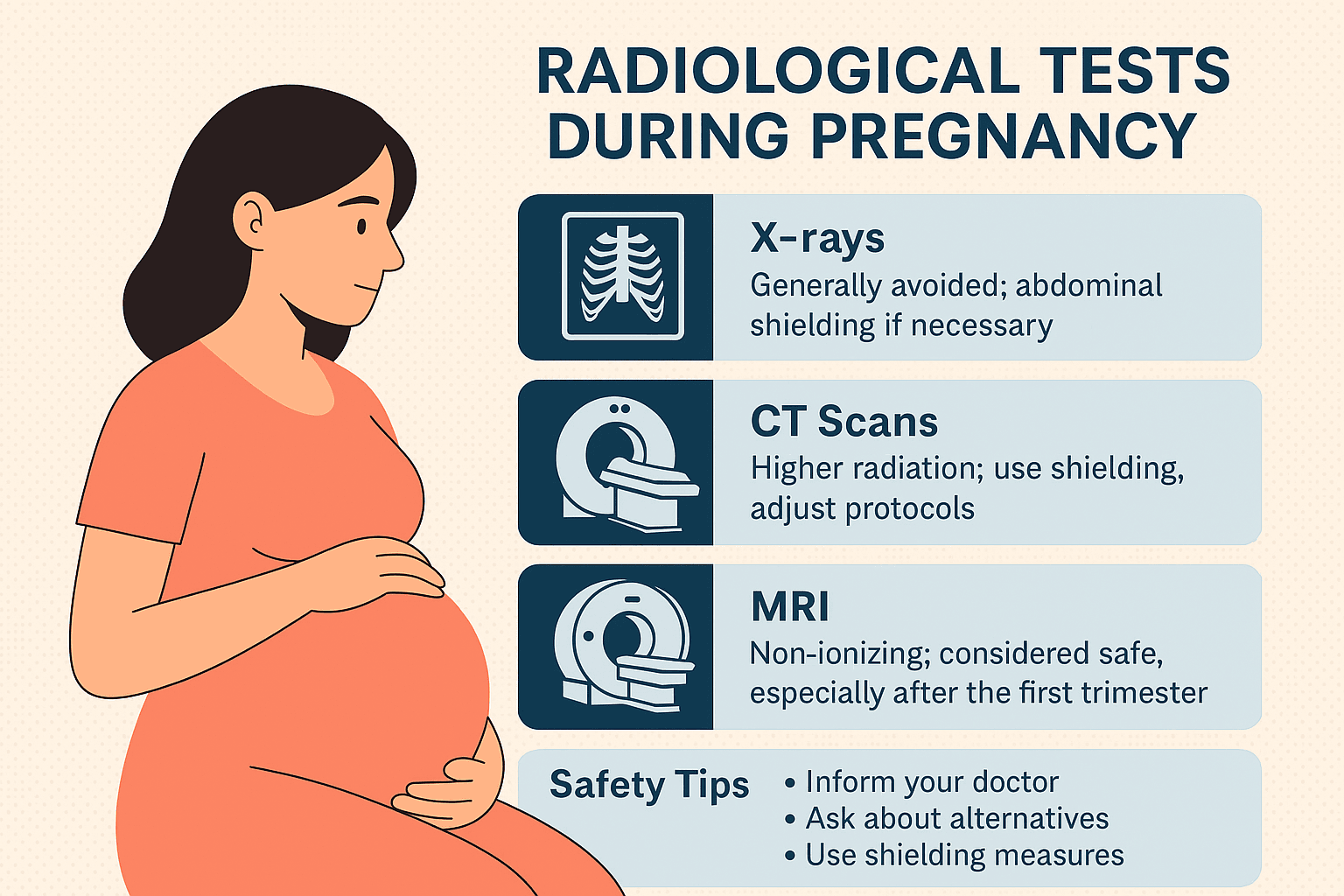
1️⃣ X-rays
- Often avoided in the abdominal and pelvic region unless absolutely essential.
- Dental X-rays and extremity X-rays (e.g., arms, legs) expose patients to minimal radiation, and experts generally consider them safer.
- Protective Measures: Use of lead aprons or abdominal shields to protect the fetus.
2️⃣ CT Scans
- Provide detailed images but involve higher radiation doses compared to X-rays.
- If a diagnosis is crucial (e.g., suspected appendicitis or trauma), doctors adjust protocols to minimize fetal exposure.
- Abdominal CT carries more risk than chest or head CT.
3️⃣ MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- Uses magnetic fields and radio waves—no ionizing radiation.
- Generally considered safe during pregnancy, especially after the first trimester.
- However, doctors usually avoid using MRI with gadolinium contrast unless absolutely necessary because they have not fully established its safety in pregnancy.
⚖️ How Doctors Balance Benefits and Risks
Doctors weigh several factors before recommending a radiological test:
✔️ Is the test critical for diagnosing a potentially serious condition?
✔️ Can alternative imaging (like ultrasound) provide the same information?
✔️ What protective steps can be taken to minimize fetal exposure?
Key Principle: If the mother’s health is at risk, and diagnosis cannot be delayed, the benefits of imaging often outweigh potential risks.
✅ Safety Tips for Expecting Mothers
🔹 Always inform your doctor and the radiology team if you’re pregnant or suspect pregnancy.
🔹 Ask about alternative tests like ultrasound or MRI without contrast.
🔹 Ensure shielding measures (lead aprons) are used if X-rays or CT scans are unavoidable.
🔹 Don’t refuse a medically necessary test out of fear—untreated conditions could pose greater risks to both mother and baby.
🔄 Alternatives to Radiological Tests
🌟 Ultrasound
- Safe and widely used during pregnancy.
- Ideal for examining soft tissues, monitoring fetal development, and diagnosing many conditions.
🌟 MRI (Non-contrast)
- Preferred for detailed imaging when ultrasound results are inconclusive.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
📌 Are X-rays during pregnancy always dangerous?
No. Most single diagnostic X-rays involve very low radiation doses that pose minimal risk. Dental X-rays, for example, are considered safe with proper shielding.
📌 Is MRI safer than CT during pregnancy?
Yes. MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a preferred option if advanced imaging is required.
📌 What happens if I had an X-ray before knowing I was pregnant?
In most cases, the radiation dose is too low to cause harm. Inform your doctor so they can assess and reassure you.
📌 Can contrast agents be used during pregnancy?
Doctors generally avoid using gadolinium-based contrasts in MRI and may use iodinated contrast for CT cautiously only when absolutely necessary.
📝 Conclusion
Healthcare providers carefully consider radiological tests during pregnancy, but they perform them safely when needed. Each situation is unique, and healthcare providers take every precaution to protect the mother and baby.
The most important step? Open communication with your medical team. Together, you can make decisions that ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and child.