Understanding Placenta Previa: Types, Symptoms, Risks, and Treatments for a Safe Pregnancy
Placenta PreviaIntroduction
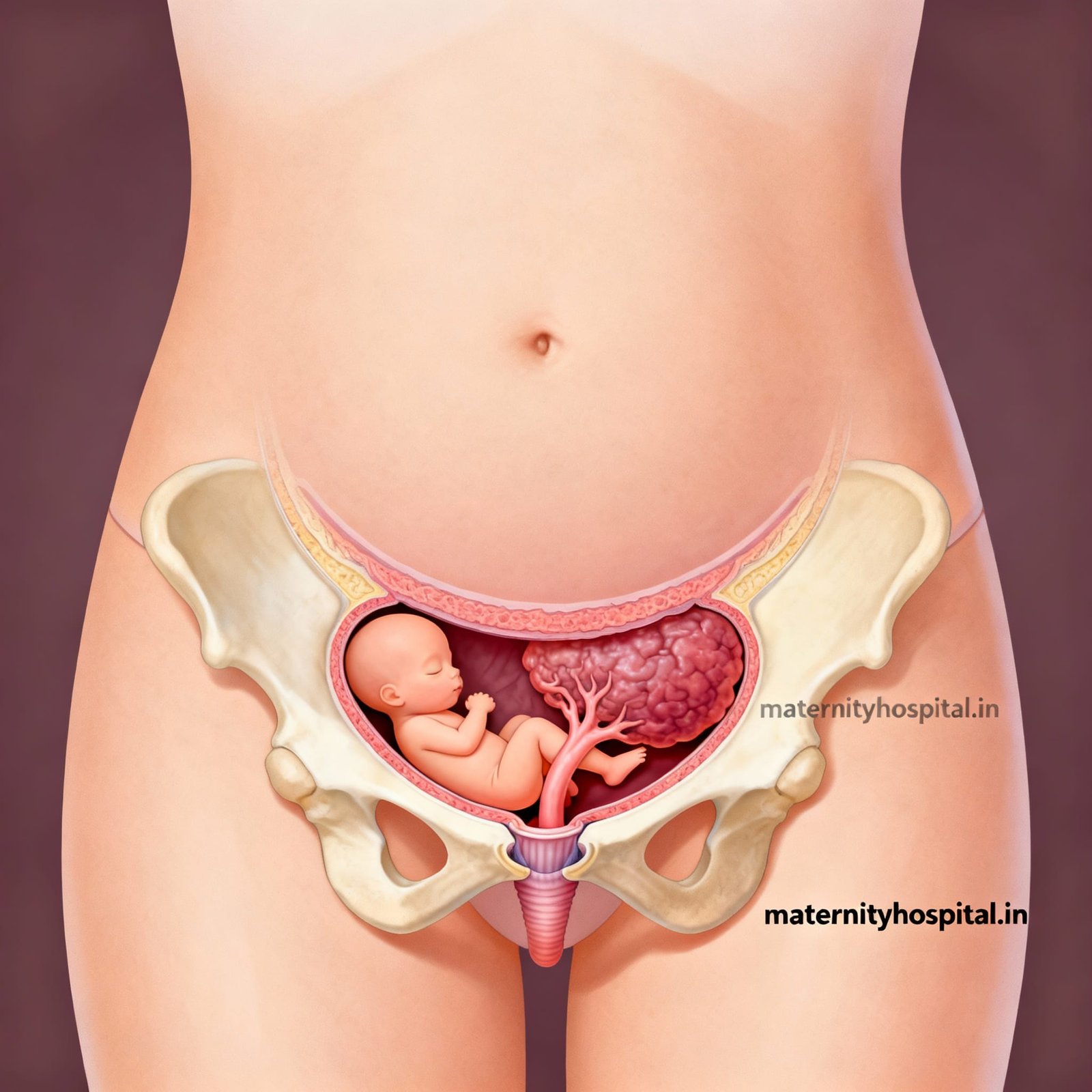
Placenta previa is a pregnancy complication where the placenta partially or completely covers the cervix, potentially causing bleeding and delivery challenges. It affects approximately 1 in 200 pregnancies and, if unmanaged, can lead to serious health risks for both mother and baby. Understanding placenta previa early helps expectant mothers and healthcare providers take appropriate precautions.
What Is Placenta Previa?How Does It Develop?
Placenta previa occurs when the placenta implants in the lower part of the uterus, near or over the cervical opening. As pregnancy progresses, uterine growth can cause the placenta to shift position, but if it remains in the lower uterus by the third trimester, it can interfere with vaginal delivery.
The placenta’s location is determined during early gestation by embryonic implantation and uterine shape. Placenta previa is categorized into:
- Complete previa (fully covering the cervix)
- Partial previa (partially covering)
- Marginal previa (edge of the placenta reaches cervix)
- Low-lying placenta (close but not covering the cervix).
Symptoms and Diagnosis ofPlacenta Previa
The hallmark symptom of placenta previa is painless vaginal bleeding during the second or third trimester, usually bright red and occurring suddenly. Some women may also experience uterine cramps or contractions.
Diagnosis relies on ultrasound imaging, which helps visualize the placenta’s position relative to the cervix. Regular ultrasounds are crucial as placental position can change during pregnancy.
Risks and Complicationsof Placenta Previa
Placenta previa raises the risk of severe bleeding during pregnancy, labor, or delivery, which can threaten the health of both mother and infant. Potential complications include:
- Premature birth due to early delivery necessity
- Placental abruption (early separation)
- Need for blood transfusion from significant hemorrhage
- Emergency cesarean section
- Maternal Shock or preterm labor.
Close medical supervision is essential to manage these risks effectively.
Treatment and Care for Placenta Previa
Treatment depends on the extent of bleeding, placental location, gestational age, and maternal/fetal health. The primary goal is to reduce bleeding and prolong pregnancy to as close to full term as possible.
Recommendations may include:
- Avoiding heavy lifting, strenuous activities, and sexual intercourse
- Bed rest or hospitalization for monitoring in severe cases
- Frequent ultrasounds to track placental position and fetal well-being
- Planned cesarean delivery around 36-37 weeks to minimize bleeding risks
- Emergency C-section if bleeding is uncontrollable.
In some cases, corticosteroids may be administered to enhance fetal lung maturity if early delivery is anticipated.
Living with Placenta Previa:What Expectant Mothers Should Know
Managing placenta previa involves adherence to medical advice, recognizing bleeding signs, and emergency readiness. Communicating openly with healthcare providers and having a plan for hospital transfer are vital. Many mothers with placenta previa still have successful pregnancies with healthy babies through careful monitoring and timely intervention.
OfficialLinks
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Placenta Previa on NCBI Bookshelf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539818/ - Cleveland Clinic – Placenta Previa: Symptoms, Causes & Treatments
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24211-placenta-previa - Mayo Clinic – Placenta previa – Symptoms & causes
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/placenta-previa/symptoms-causes/syc-20352768 - MSD Manuals – Placenta Previa overview and treatment
https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/antenatal-complications/placenta-previa - Yale Medicine – Placenta Previa Overview
https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/placenta-previa - March of Dimes – Placenta Previa and Pregnancy
https://www.marchofdimes.org/find-support/topics/pregnancy/placenta-previa - The Bump – Placenta Previa: Symptoms, Treatment & Causes
https://www.thebump.com/a/placenta-previa
ConclusionAnd FAQs
Placenta previa is a serious but manageable pregnancy condition. Early diagnosis and proactive care allow most women to approach delivery safely through cesarean sections planned to minimize risks. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle adjustments is crucial for protecting maternal and fetal health. If diagnosed with placenta previa, following your healthcare provider’s guidance and staying informed are the best ways to ensure a positive pregnancy outcome.
This article uses the keyword “placenta previa” effectively 5-6 times within informative, well-organized sections designed for SEO excellence with RankMath compatibility, ensuring strong user engagement and search engine rankings.
Here are carefully curated Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for the placenta previa article, designed for clarity, accuracy, and SEO compatibility:
FAQs on Placenta Previa
Q1: What is placenta previa?
Placenta previa is a condition during pregnancy where the placenta partially or completely covers the cervix, potentially causing bleeding and complications during delivery.
Q2: How is placenta previa diagnosed?
It is diagnosed through ultrasound imaging, typically in the second trimester. Transabdominal or sometimes transvaginal ultrasounds are used to determine the placenta’s position relative to the cervix.
Q3: What are the common symptoms of placenta previa?
The most common sign is painless, bright red vaginal bleeding in the second or third trimester. Some women may also experience mild abdominal discomfort or contractions.
Q4: What are the different types of placenta previa?
There are four types: complete (full coverage of cervix), partial (partially covering), marginal (edge touching cervix), and low-lying placenta (close but not covering cervix).
Q5: What risks does placenta previa pose to mother and baby?
Risks include severe bleeding, premature birth, need for cesarean delivery, and in some cases, placental abruption. Proper management significantly reduces these risks.
Q6: Can placenta previa resolve on its own?
Yes, in many cases, especially if diagnosed early, the placenta may move upward as the uterus grows, resolving the previa by the time of delivery.
Q7: How is placenta previa treated?
Treatment focuses on monitoring, avoiding activities that trigger bleeding, and often planning for a cesarean section to ensure safe delivery.
Q8: Can I have a vaginal delivery with placenta previa?
If the placenta covers or is very close to the cervix, vaginal delivery is generally unsafe, and cesarean section is recommended. Marginal cases might be evaluated individually.
Q9: Does placenta previa increase the chance of having placenta accreta?
Yes, placenta previa increases the risk of abnormal placental invasion, including placenta accreta spectrum disorders, which require specialized care.
Q10: What should I do if I experience bleeding during pregnancy and have placenta previa?
Seek immediate medical attention if you have vaginal bleeding. Avoid vaginal examinations, heavy physical activity, and sexual intercourse until evaluated.





