Explore the amazing pregnancy development stages from 1 to 9 months
Introduction:The Miracle of Monthly Pregnancy Development Stages
Pregnancy is one of life’s most profound and transformative journeys, a nine-month odyssey filled with wonder, anticipation, and incredible change. From the moment of conception, a tiny cluster of cells embarks on a meticulously orchestrated process, evolving into a fully formed human being. For expecting parents, understanding these pregnancy development stages can be both reassuring and awe-inspiring, offering a glimpse into the intricate miracle unfolding within.
This ultimate guide will take you through each month of pregnancy, from the very first stirrings of life to the final preparations for birth. We’ll explore the remarkable milestones of fetal growth, the significant changes happening in the mother’s body, and key insights into what to expect along the way. Whether you’re a first-time parent or looking to deepen your understanding, join us as we uncover the magic and science behind each pregnancy development stage, month by month. Prepare to be amazed by the intricate dance of nature that culminates in the arrival of your little one.
The First Trimester –The Miracle of Monthly Pregnancy Development Stages
The first trimester is a period of rapid and fundamental development, often before many even realize they are pregnant. It’s a time when the foundational structures of the baby are formed, and the mother’s body begins its monumental transformation.
Month 1: Conception & Early Formation (Weeks 1-4)
The journey officially begins with fertilization, usually around week 2 of your cycle.
- Fetal Development:
- Conception: A sperm fertilizes an egg, forming a single-celled zygote.
- Implantation: The zygote rapidly divides and travels down the fallopian tube to implant in the uterine wall, becoming an embryo.
- Germ Layers: By the end of the month, the embryo forms three distinct germ layers: the ectoderm (which will become the brain, spinal cord, nerves, skin, hair), mesoderm (bones, muscles, heart, blood vessels), and endoderm (lungs, intestines, urinary system).
- Amniotic Sac & Placenta: The amniotic sac, which will house the baby, and the placenta, vital for nourishment and waste removal, begin to form.
- Heartbeat: A primitive heart tube forms and begins to beat by week 3-4, often before it can even be detected on ultrasound.
- Maternal Changes:
- Key Milestones & Tips:
Month 2: Organogenesis in Full Swing (Weeks 5-8)
This is a critical period for organ development.
- Fetal Development:
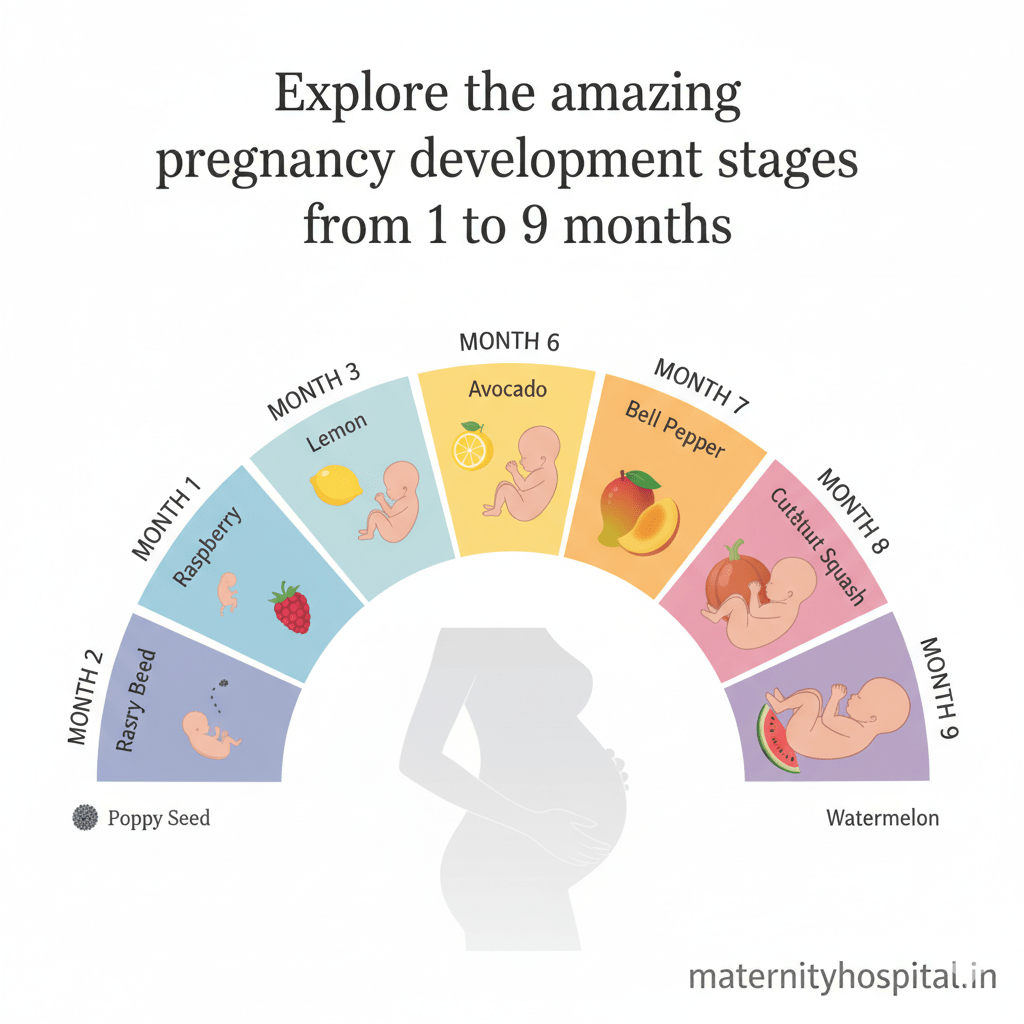
- Size: The embryo is about the size of a raspberry (around 1 inch long by the end of month 2).
- Heart: The heart is now beating rhythmically and becoming more developed.
- Brain & Spinal Cord: The neural tube closes, forming the brain and spinal cord.
- Limbs: Tiny limb buds appear, which will develop into arms and legs. Fingers and toes begin to form, though they are webbed.
- Facial Features: Eyes, ears, nose, and mouth start to develop.
- Major Organs: Lungs, liver, pancreas, and kidneys begin to form.
- Movement: The embryo starts to make small, jerky movements, though you won’t feel them yet.

- Maternal Changes:
- Morning Sickness: Nausea and vomiting (morning sickness) are very common.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness due to hormonal changes and the body’s hard work.
- Food Aversions/Cravings: Changes in appetite.
- Breast Changes: Breasts may feel fuller, heavier, and more tender.
- Key Milestones & Tips:
- Your first ultrasound may reveal the heartbeat!
- Focus on small, frequent meals to combat morning sickness.
- Prioritize rest.
Month 3: The Fetus Emerges (Weeks 9-13)
By the end of this month, the most critical period of organ development is complete, and the embryo is officially called a fetus.
- Fetal Development:
- Size: The fetus is about 2.5-3 inches long and weighs about 1 ounce (size of a plum).
- Organ Function: All major organs are formed and beginning to function.
- Limbs & Digits: Arms, hands, fingers, legs, feet, and toes are fully formed. Nails are developing.
- Facial Definition: Eyes are widely spaced, but eyelids are fused shut. Ears are almost in their final position.
- Sex Organs: External sex organs begin to develop, though it’s usually too early to determine sex via ultrasound.
- Reflexes: The fetus can open and close its fists and mouth, and even hiccup.
- Maternal Changes:
- Morning Sickness Improvement: Nausea often starts to subside towards the end of this month.
- Uterus Growth: Your uterus is now about the size of a grapefruit and may start to show a tiny bump.
- Energy Levels: Energy may begin to return.
- Key Milestones & Tips:
The first trimester, though challenging for many mothers, lays the entire foundation for your baby’s life, marking incredible initial pregnancy development stages.
The Second Trimester –Weeks 14-27 (Months 4-6)
Often called the “golden trimester,” this period brings increased energy for the mother and significant growth and movement for the baby.
Month 4: Growth Spurt & Movement Begins (Weeks 14-17)
- Fetal Development:
- Size: The fetus grows rapidly, reaching about 4-5 inches and weighing around 4 ounces (size of an avocado).
- Skin & Hair: Fine hair (lanugo) covers the body, and eyebrows/eyelashes begin to grow.
- Reflexes: Sucking and swallowing reflexes develop.
- Skeletal Development: Bones are hardening.
- Kidney Function: Kidneys are producing urine.
- Fetal Movement (Quickening): You may feel the first flutters or “quickening” – like gas bubbles or butterfly wings. This is a thrilling milestone!
- Maternal Changes:
- Key Milestones & Tips:
- Feeling the first baby movements is a magical moment.
- Start thinking about baby names!
Month 5: Development of Senses & Detailed Scan (Weeks 18-21)
- Fetal Development:
- Size: The fetus is now about 6-8 inches long and weighs around 1 pound (size of a large mango).
- Sensory Development: Hearing develops significantly. The baby can now hear your voice, heartbeat, and external sounds.
- Skin Protection: A waxy coating called vernix caseosa begins to protect the skin.
- Sleep-Wake Cycles: The baby develops more regular sleep and wake patterns.
- Sex Determination: Gender can usually be determined during ultrasound, if desired.
- Maternal Changes:
- Key Milestones & Tips:
- The anatomy scan (mid-pregnancy ultrasound) usually happens around 18-22 weeks, checking the baby’s growth and development.
- Stay active with gentle exercise like walking or swimming.

Month 6: Facial Features & Lung Development (Weeks 22-27)
- Fetal Development:
- Size: The fetus is about 10-12 inches long and weighs 1.5-2 pounds (size of an eggplant).
- Facial Features: Eyebrows and eyelids are distinct, and the eyes can open and close.
- Lung Development: Lungs continue to mature, producing surfactant (a substance critical for breathing outside the womb).
- Hearing: Responds to sounds more clearly.
- Movement: Movements become stronger and more coordinated. You’ll feel kicks and punches!
- Maternal Changes:
- Increased Fetal Movement: You’ll feel distinct kicks and jabs.
- Sleep Disruption: Finding a comfortable sleeping position may become challenging.
- Skin Changes: Stretch marks may appear, and the linea nigra (dark line on the abdomen) might become more prominent.
- Key Milestones & Tips:
- Start monitoring fetal movements regularly.
- Begin planning for your baby’s arrival, including nursery setup and childbirth classes.
The second trimester is often a period of growing excitement and connection, as the baby becomes a more active presence in the mother’s life. These pregnancy development stages bring significant joy and anticipation.
The Third Trimester –Weeks 28-40+ (Months 7-9)
The final trimester is a period of rapid weight gain for the baby, lung maturation, and preparation for birth, while the mother experiences increasing physical demands.
Month 7: Brain Growth & Lung Maturation (Weeks 28-31)
- Fetal Development:
- Size: The baby is about 14-16 inches long and weighs 2.5-3.5 pounds (size of a large cabbage).
- Brain Development: The brain develops rapidly, increasing in size and complexity.
- Lung Maturity: Lungs continue to mature, though still not fully ready for life outside the womb.
- Fat Accumulation: Fat layers begin to form under the skin, preparing for temperature regulation after birth.
- Sensory Awareness: The baby reacts more strongly to light, sound, and pain.
- Practice Breathing: The baby practices breathing movements.
- Maternal Changes:
- Increased Discomfort: Backaches, leg cramps, heartburn, and shortness of breath may worsen.
- Fetal Activity: Movements are strong and distinct.
- Frequent Urination: Increased pressure on the bladder.
- Key Milestones & Tips:
- Begin thinking about your birth plan.
- Pack your hospital bag.
- Attend childbirth education classes.
Month 8: Position & Rapid Weight Gain (Weeks 32-35)
- Fetal Development:
- Size: The baby is about 16-18 inches long and weighs 4-5.5 pounds (size of a honeydew melon).
- Positioning: Most babies start to turn head-down in preparation for birth.
- Organ Maturation: All major organs are fully developed, except for the lungs, which are still maturing.
- Bones: Bones are fully developed but still soft.
- Reflexes: Blinking, grasping, and rooting reflexes are present.
- Maternal Changes:
- Shortness of Breath: The uterus pushes up against the diaphragm.
- Swelling: Swelling (edema) in ankles, feet, and hands is common.
- Fatigue Returns: Energy levels may dip again.
- Braxton Hicks Contractions: May become more frequent and noticeable.
- Key Milestones & Tips:
- Regular prenatal check-ups become more frequent.
- Finalize baby preparations at home.
Month 9: Full Term & Ready for Arrival (Weeks 36-40+)
- Fetal Development:
- Size: The baby is now considered full-term (from 37 weeks onwards), typically weighing 6-9 pounds and measuring 18-20 inches long (size of a small watermelon).
- Lung Maturity: Lungs are fully mature and ready for breathing outside the womb.
- Fat Stores: Sufficient fat stores are built for warmth and energy after birth.
- Antibodies: The baby receives antibodies from the mother, building its immune system.
- “Dropping” (Lightening): The baby often drops lower into the pelvis.
- Lanugo Sheds: Most of the lanugo (fine body hair) and vernix caseosa (waxy coating) have shed into the amniotic fluid.
- Maternal Changes:
- “Lightening”: You may feel a sensation of the baby dropping lower, which can relieve pressure on your lungs but increase pressure on your bladder.
- Increased Pelvic Pressure: Discomfort in the pelvic area.
- Cervical Changes: Your cervix may begin to thin (efface) and open (dilate) in preparation for labor.
- Sleep Difficulty: Finding comfortable sleep positions is challenging.
- Nesting Instinct: A sudden urge to clean and organize.
- Key Milestones & Tips:
- Your baby is ready to meet you!
- Monitor for signs of labor: regular contractions, water breaking, bloody show.
- Trust your instincts and communicate with your healthcare provider.
Each of these pregnancy development stages culminates in the incredible moment of birth, a testament to the remarkable capabilities of both mother and baby.
FAQsAbout Pregnancy Development Stages
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about pregnancy development stages.
- What are the main milestones in the first trimester?
The first trimester is crucial for the formation of all major organs, the development of the brain and spinal cord, and the establishment of the heart’s beat. The embryo officially becomes a fetus, and the amniotic sac and placenta are fully formed.
- When does the baby’s heart start beating?
The baby’s primitive heart tube begins to beat around week 3-4 of pregnancy. It can often be detected on an early ultrasound by week 6.
- What are the biggest changes a mother experiences in the second trimester?Mothers often experience increased energy, a reduction in morning sickness, and the exciting milestone of feeling the baby move (quickening). The baby bump becomes more prominent, and some aches and pains may begin.
- When can you feel the baby move for the first time?
Most mothers feel the first fetal movements, often described as flutters or gas bubbles, between weeks 16 and 22 of pregnancy. For first-time mothers, it’s often closer to 20-22 weeks.
- What happens in the ninth month of pregnancy?
In the ninth month (weeks 36-40+), the baby is considered full-term. Its lungs are fully mature, it has accumulated sufficient fat stores, and it typically moves into a head-down position in the pelvis. The mother experiences increasing pelvic pressure, more frequent Braxton Hicks contractions, and her cervix begins to prepare for labor.
- How does the baby prepare for birth in the final stages?
In the final stages, the baby’s lungs reach full maturity, it builds fat stores for warmth and energy, and receives antibodies from the mother for immune protection. It also typically moves into a head-down position, “dropping” into the pelvis, ready for delivery.
- Is every pregnancy development timeline exactly the same?
No, while there’s a general timeline for pregnancy development stages, every pregnancy and every baby is unique. Babies develop at their own pace, and slight variations in milestones are perfectly normal. Your healthcare provider monitors your specific progress.
- What are common discomforts during each stage of pregnancy?
- First Trimester: Fatigue, nausea/vomiting (morning sickness), breast tenderness, frequent urination.
- Second Trimester: Backaches, round ligament pain, leg cramps, heartburn, occasional Braxton Hicks contractions.
- Third Trimester: Increased fatigue, shortness of breath, swelling (edema), more frequent and intense Braxton Hicks, pelvic pressure, difficulty sleeping.
FAQsAbout Pregnancy Development Stages
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about pregnancy development stages.
- What are the main milestones in the first trimester?
The first trimester is crucial for the formation of all major organs, the development of the brain and spinal cord, and the establishment of the heart’s beat. The embryo officially becomes a fetus, and the amniotic sac and placenta are fully formed.
- When does the baby’s heart start beating?
The baby’s primitive heart tube begins to beat around week 3-4 of pregnancy. It can often be detected on an early ultrasound by week 6.
- What are the biggest changes a mother experiences in the second trimester?
Mothers often experience increased energy, a reduction in morning sickness, and the exciting milestone of feeling the baby move (quickening). The baby bump becomes more prominent, and some aches and pains may begin.
- When can you feel the baby move for the first time?
Most mothers feel the first fetal movements, often described as flutters or gas bubbles, between weeks 16 and 22 of pregnancy. For first-time mothers, it’s often closer to 20-22 weeks.
- What happens in the ninth month of pregnancy?
In the ninth month (weeks 36-40+), the baby is considered full-term. Its lungs are fully mature, it has accumulated sufficient fat stores, and it typically moves into a head-down position in the pelvis. The mother experiences increasing pelvic pressure, more frequent Braxton Hicks contractions, and her cervix begins to prepare for labor.
- How does the baby prepare for birth in the final stages?
In the final stages, the baby’s lungs reach full maturity, it builds fat stores for warmth and energy, and receives antibodies from the mother for immune protection. It also typically moves into a head-down position, “dropping” into the pelvis, ready for delivery.
- Is every pregnancy development timeline exactly the same?
No, while there’s a general timeline for pregnancy development stages, every pregnancy and every baby is unique. Babies develop at their own pace, and slight variations in milestones are perfectly normal. Your healthcare provider monitors your specific progress.
- What are common discomforts during each stage of pregnancy?
- First Trimester: Fatigue, nausea/vomiting (morning sickness), breast tenderness, frequent urination.
- Second Trimester: Backaches, round ligament pain, leg cramps, heartburn, occasional Braxton Hicks contractions.
- Third Trimester: Increased fatigue, shortness of breath, swelling (edema), more frequent and intense Braxton Hicks, pelvic pressure, difficulty sleeping.
ConclusionAbout Pregnancy Development Stages
Conclusion: Celebrating Each Milestone of Pregnancy Development Stages
The journey through the pregnancy development stages, from the microscopic beginnings in month one to the readiness for birth in month nine, is nothing short of miraculous. Each passing week and month brings forth incredible transformations, both within your growing baby and in your own body. Understanding these changes can transform apprehension into excitement and curiosity into profound connection.
Remember that while this guide provides a general roadmap, your pregnancy journey is uniquely yours. Embrace the subtle shifts, celebrate the big milestones, and always communicate any questions or concerns with your healthcare provider. As you anticipate meeting your little one, take comfort in knowing that your body is a testament to nature’s most extraordinary design, meticulously preparing for the arrival of your child, one amazing month at a time. The miracle of life truly unfolds in these intricate pregnancy development stages.
Official External Link Placeholder
For more in-depth, trusted medical information on fetal development and pregnancy health, please consult official health resources.
- Learn more about stages of pregnancy from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) at: [Link to ACOG website on Stages of Pregnancy or Fetal Development – e.g.,
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/how-your-fetus-grows-during-pregnancy]